The family of NdFeB is revealed: sinter-bond-hot pressed

NdFeB permanent products according to the production process can be divided into sintered NdFeB, bonded NdFeB and hot pressed NdFeB. Due to the different production processes, they have great differences in magnetic properties, post processing and application of products. Before we have made a systematic introduction to the sintered NdFeB, and then we will introduce bonded and hot-pressed NdFeB, and three different types of NdFeB products in property and application comparison.
Bonded NdFeB
Bongding NdFeB appeared around the 1970s, when SmCo was commercialized, and the market for sintered NdFeB permanent magnets was good, but it was difficult to precisely process them into special shapes, and in the process of processing was easy to appear cracking, damage, drop edge, drop angle and other problems,but also not easy to assemble, so that its application was limited. To solve this problem, a permanent magnet is crushed and mixed with plastic and pressed into shape in a magnetic field, which is probably the most primitive manufacturing methods of bonded NdFeB. Bonded NdFeB are widely used because of the advantages of low cost, high dimensional precision, large shape freedom, good mechanical strength and light weight.
One: Production process:
Bonded NdFeB is a permanent magnet powder and rubber or light weight of plastic and other bonding materials mixed, according to user requirements directly into a variety of shapes of permanent magnet parts.
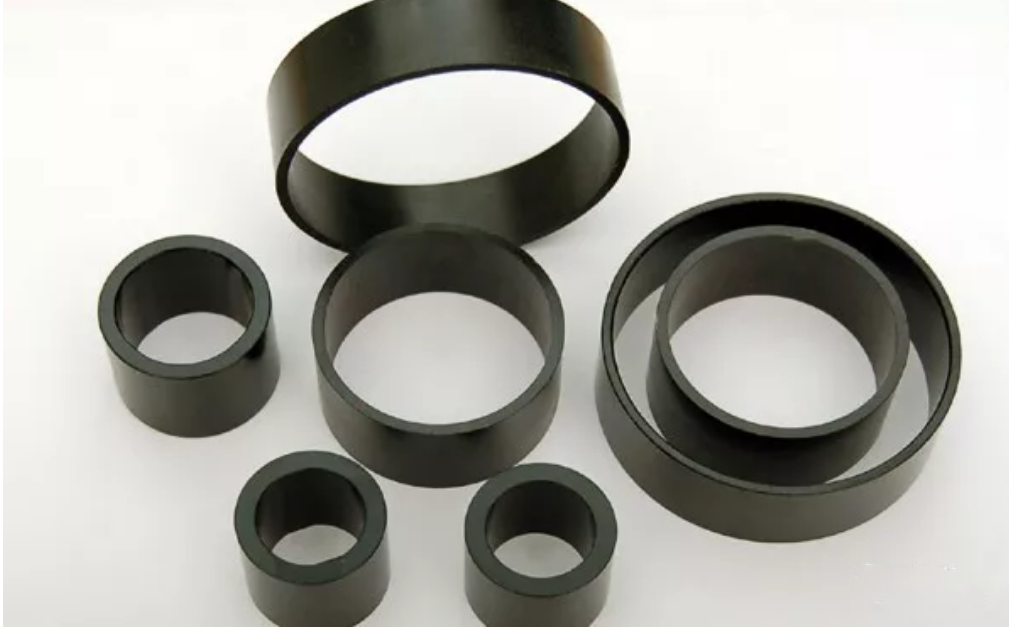


The preparation of magnetic powder is the key process of processing NdFeB permanent magnet, the properties of magnetic particles directly affect the magnetic properties of permanent magnets. The preparation methods of NdFeB magnetic powder include mechanical crushing, rapid melting, HDDR, gas spray and mechanical alloying etc. At present, the mainstream process adopts HDDR method, which is to prepare high-performance of rare earth permanent magnetic powder through the process of hydrogenation - decomposition -dehydrogenation -recombination: firstly, the alloy is broken into coarse powder, loaded into a vacuum furnace, and crystallized at a certain temperature, the alloy absorbs hydrogen and produces disproportionation reaction, and then the hydrogen is extracted recombined into rare earth permanent magnetic powder with very small grains. In this way, fine grains with average particle size of 0.3μm can be obtained, and magnetic particles with high coercivity can be obtained.
At pressent, there are four kinds of pressing moulding techniques for bonded NdFeB: calendering, injection molding, extrusion molding and molding, among which calendaring and injection are more mainstream.
1、Calendering is the process of evenly mixing magnetic powder and binder in a certain volume proportion, rolling them to the required thickness and then curing them into finished product. Vinyl resins and nitrile butadiene rubber are commonly used as adhesives, the product surface needs to be coated.
2. Injection molding is the magnetic powder and binder(thermoplastic resin), through heating mixing, granulation, drying, and then send to the heating chamber through the spiral guide rod heating, at a certain speed into the mold cavity molding, cooling after the final product, due to the high content of resin, a protective film can be formed on the surface of the magnet, so it is generally no necessary to do surface preservative treatment, unless the surface preservative capability is required.
3.Extrusion molding is basically the same as injection molding , with the only difference being that the heated granules are extruded into the mold through a hole for continuous molding.
4. molding is to mix magnetic powder and binder in proportion, granulate and add a certain amount of coupling agent, press molding in the mold, in 120°~150° curing, the final product.
Two: properties of product:
Add adhesive, magnetic properties are lower than sintered NdFeB: bonding NdFeB magnes are to used to bond the magnetic powder into a larger magnet, generally its density is only 80% of the theoretical, and sintered NdFeB magnet through the complex processes of high temperature heating, so on the magnetic property, bonded NdFeB is weaker than sintered NdFeB.
The below chart is the common product grade and property of our combined network resources integration calendaring and injection bonded NdFeB, for your reference.

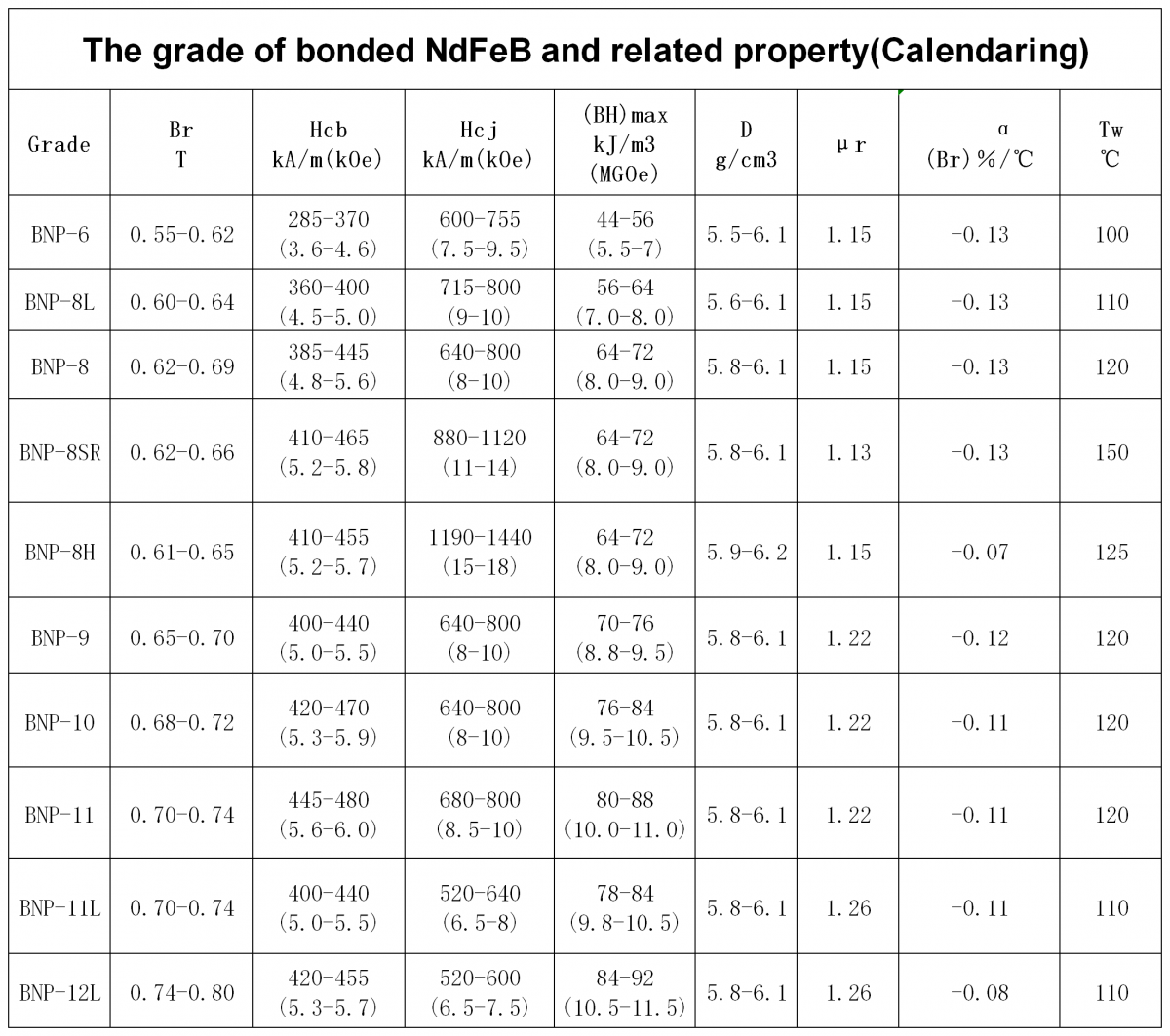
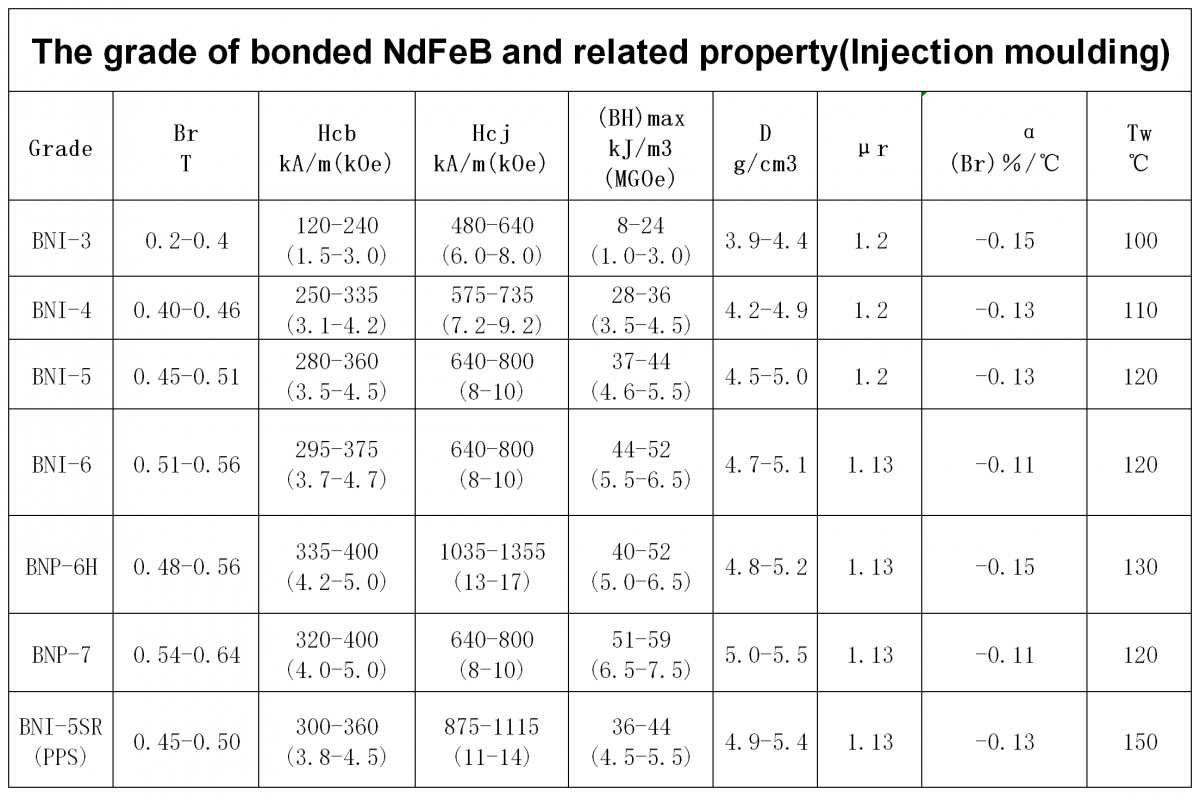

In addition, the government standard for bonded NdFeB permanent magnetic materials is GB/T 18880-2012, you can also refer to.
High product precision, large type freedom: sintered NdFeB is produced with the method of powder sintering, general sintering only can produce blank, and then though mechanical processing ( such as line cutting、section、grinding etc.)to become a variety shapes of magnets. Compared with sintered NdFeB, the production process of bonded NdFeB permanent magnet is simpler, without secondary processing, and its products have high dimensional precision and no deformation, in the mean time large shape of freedom, according to the actual use of the demand to manufacture a variety of shapes of products , such as long strip, sheet, tube, circular ring or other complex shapes, easy to mass automatic production and high mechanical intensity of the products.
Isotropic magnet for easy magnetization in any direction: bonded NdFeB is an isotropic magnet with the same magnetism in all directions, so it is easy to make a multiple or even an infinite number of poles for overall magnets, which is often hard to achieve for sintered NdFeB magnets.
Three : product application
The magnetic property of bonded NdFeB is lower than sintered NdFeB, but because of its convenient manufacturing multipole magnetized ring magnet, excellent consistency and uniformity of performance, and easy to be integrated with other metal or plastic parts, much higher than the magnetic properties of bonded ferrite, is widely used in all kinds of micro motor and sensor systems. The specific application of bonded NdFeB can be divided into:
Digital products: hard drive magnets (HDD)- this is currently the largest application for bonded NdFeB.
Office OA products: printer drive motor, scanner motor, photocopier synchronous motors, laser printer magnetic roller etc.
Automobile motor and magnetic sensor products: including EPS power steering sensor magnets, wiper motors, window-adjusting motors, seat regulator motors etc.
Other types of industrial and household motors: mainly including all kinds of servo motors, electrical motors for power tools, air conditioning motors etc.


Due to the huge difference in magnetic properties and forming, the intersection of bonded NdFeB and sintered NdFeB is not large. Bonded NdFeB is mainly used in the field of hard disk drive spindle motor and micro-motor with small power, and sintered NdFeB is more used in the field of driving motor with large power.
